Vitamin K Dependent Coagulation Factors

The blood clotting factors of newborn babies are roughly 30 60 that of adult values.
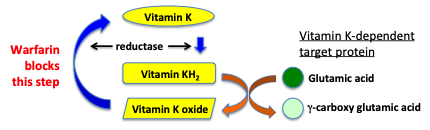
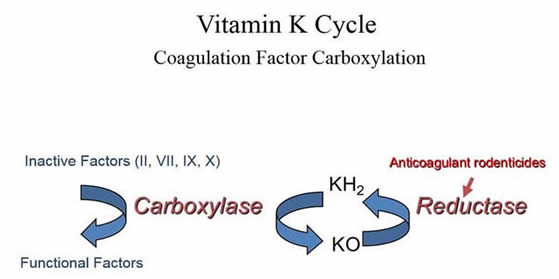
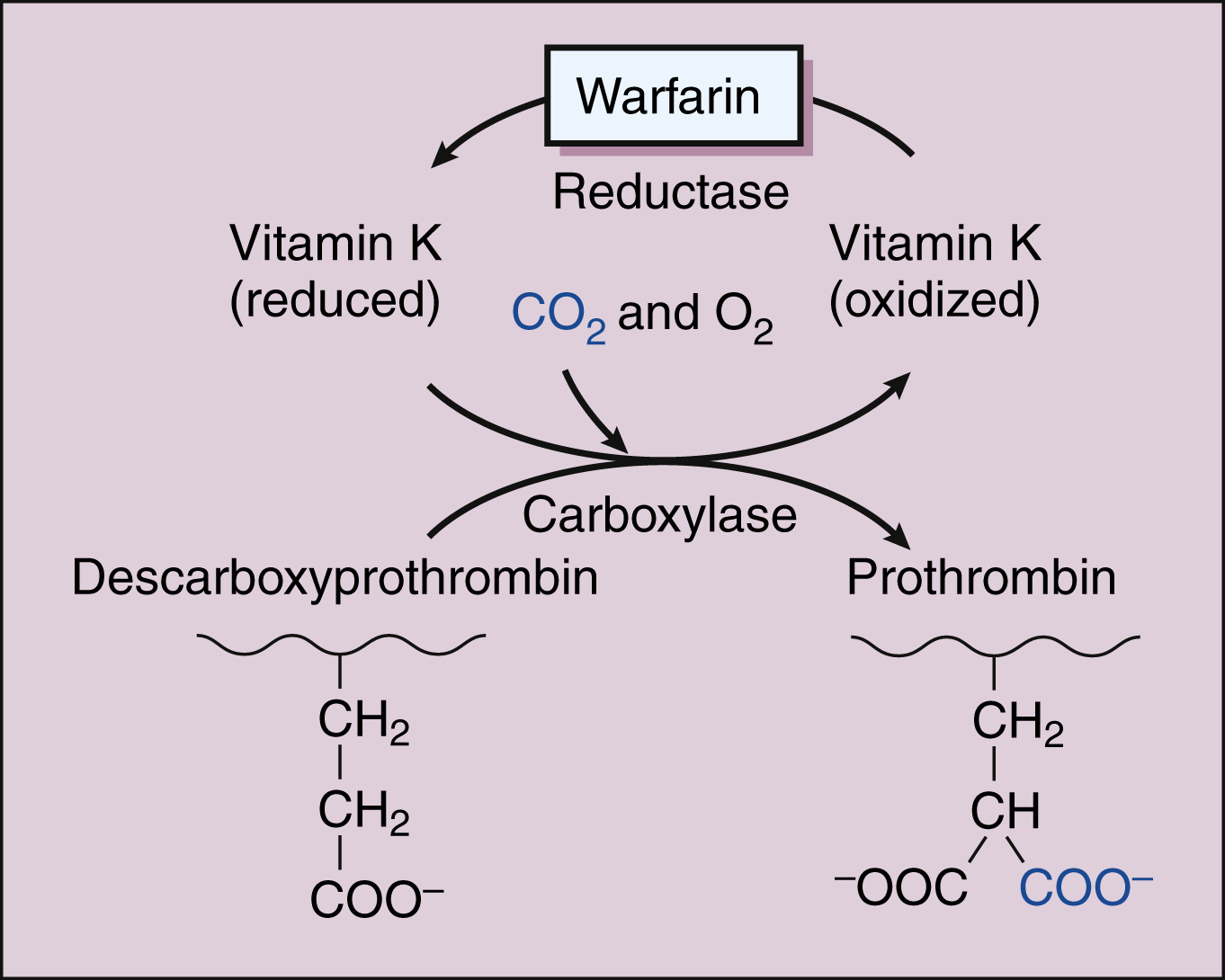
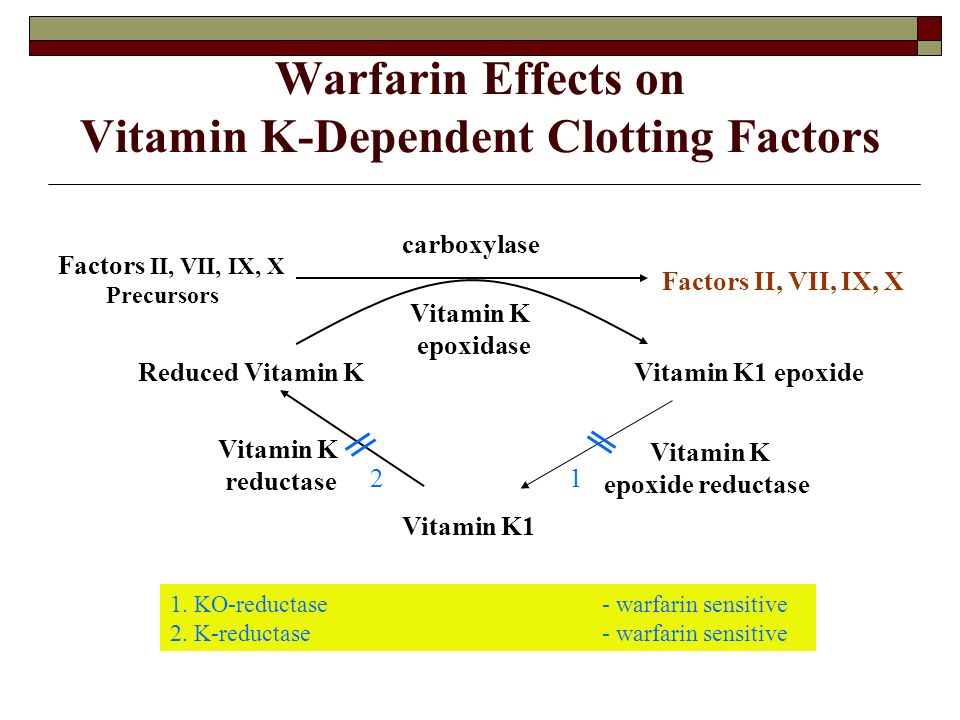
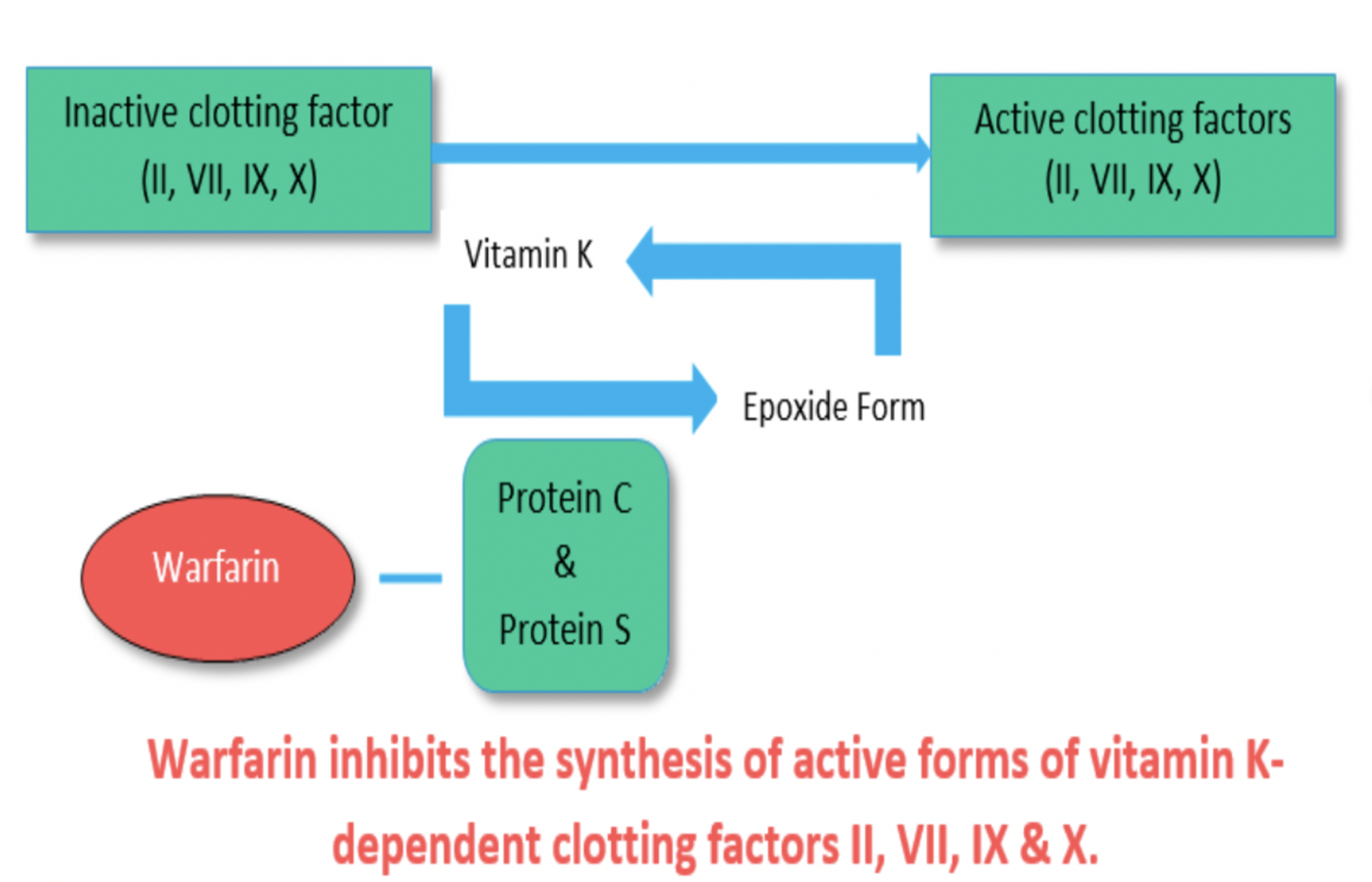
Vitamin k dependent coagulation factors. Without enough vitamin k not enough vitamin k dependent coagulation proteins are carboxylated. Defects in carboxylation are mainly associated with bleeding disorders. This appears to be a consequence of poor transfer of the vitamin across the placenta and thus low fetal plasma vitamin k. Warfarin affects the vitamin k dependent clotting factors ii vii ix x and protein c and protein s whereas heparin and related compounds increase the action of antithrombin on thrombin and factor xa.
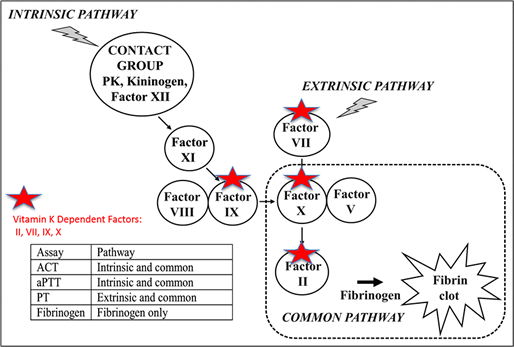
Some members are already in clinical use such as lepirudin. The vitamin k dependent coagulation factors are factors ii vii ix x proteins c and s. Deficiency of all vitamin k dependent clotting factors leads to a bleeding tendency that is usually reversed by oral administration of vitamin k. Vitamin k is important in the steps involving protein factor ii vii ix and x 1.
In turn this inhibits the coagulation cascade and blocks clot formation. Factor ii is alternatively named prothrombin. 127 129 these rare autosomal recessive disorders have an estimated incidence of 1. Vitamin k dependent clotting factor.
Also anticoagulation proteins c s and z as well as osteocalcin and the matrix gla protein depend on vitamin k. Four other proteins. Warfarin 4 hydroxycoumarin inhibits the synthesis of vitamin k dependent coagulation factors including factors ii vii ix and x as well as proteins c and s. Vitamin k dependent carboxylation is a posttranslational modification essential for the biological function of coagulation factors.
Combined deficiency of the vitamin k dependent factors may result from missense mutations in the genes for vitamin k reductase vkorc 1 or gamma glutamyl carboxylase. Acquired forms of the disorder can be caused by intestinal malabsorption of vitamin k. 4 6 too much vitamin k can overcome warfarin s anticoagulant effects which can lead to potentially deadly clots. Prothrombin alone needs vitamin k to modify 10 different regions within the protein for functionality.
Familial multiple coagulation factor deficiency is rare. Any of a group of coagulation factor proenzymes factors ii vii ix and x produced in the liver that contain multiple residues of gamma carboxyglutamic acid an amino acid produced by the post translational action of a vitamin k dependent gamma carboxylase on certain glutamyl residues. A newer class of drugs the direct thrombin inhibitors is under development. Occurrence of vitamin k deficiency bleeding in the first week of the infant s life is estimated at 0 25 1 7 with a prevalence of 2 10 cases per 100 000 births.