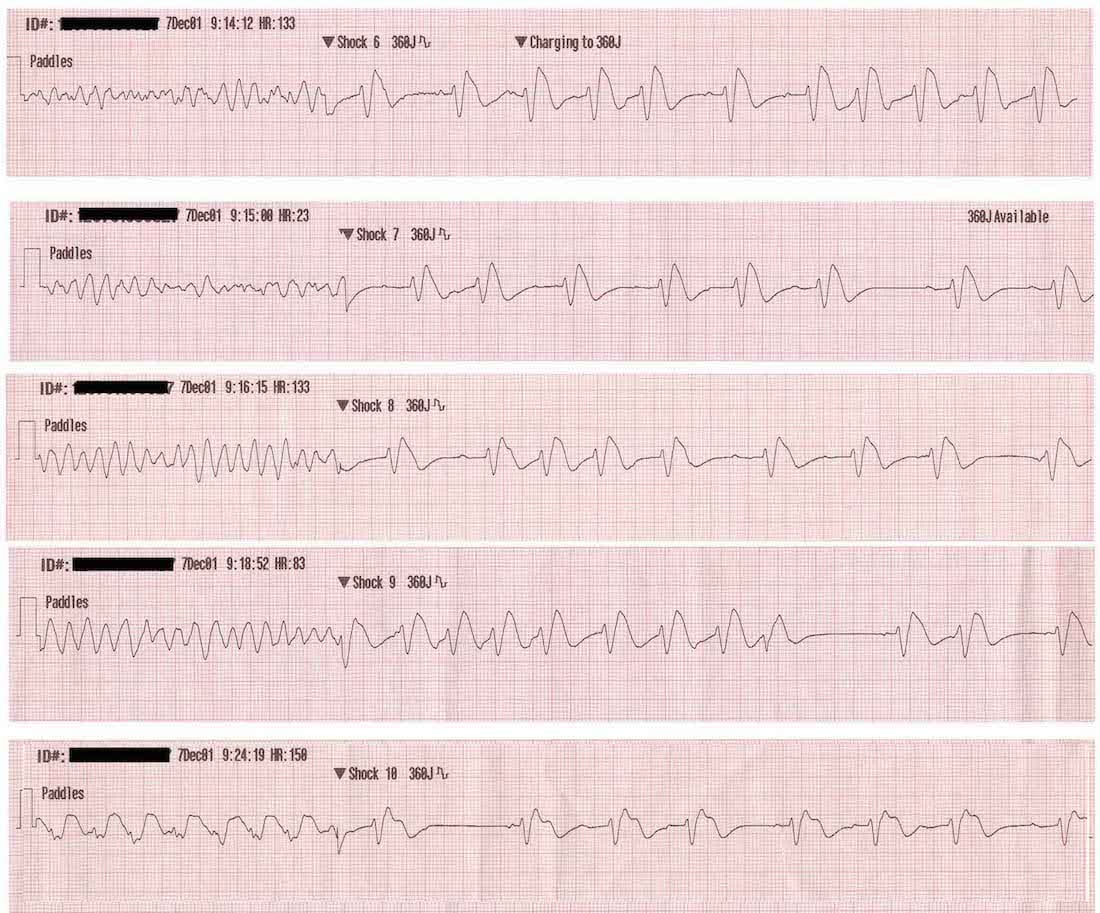
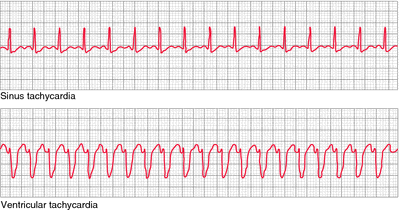
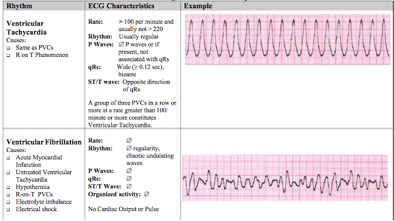
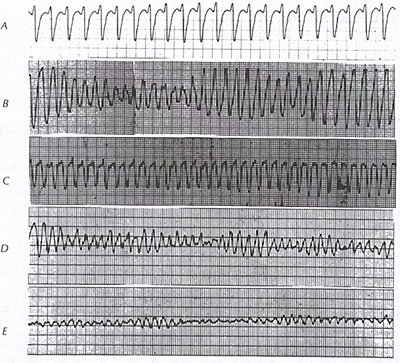
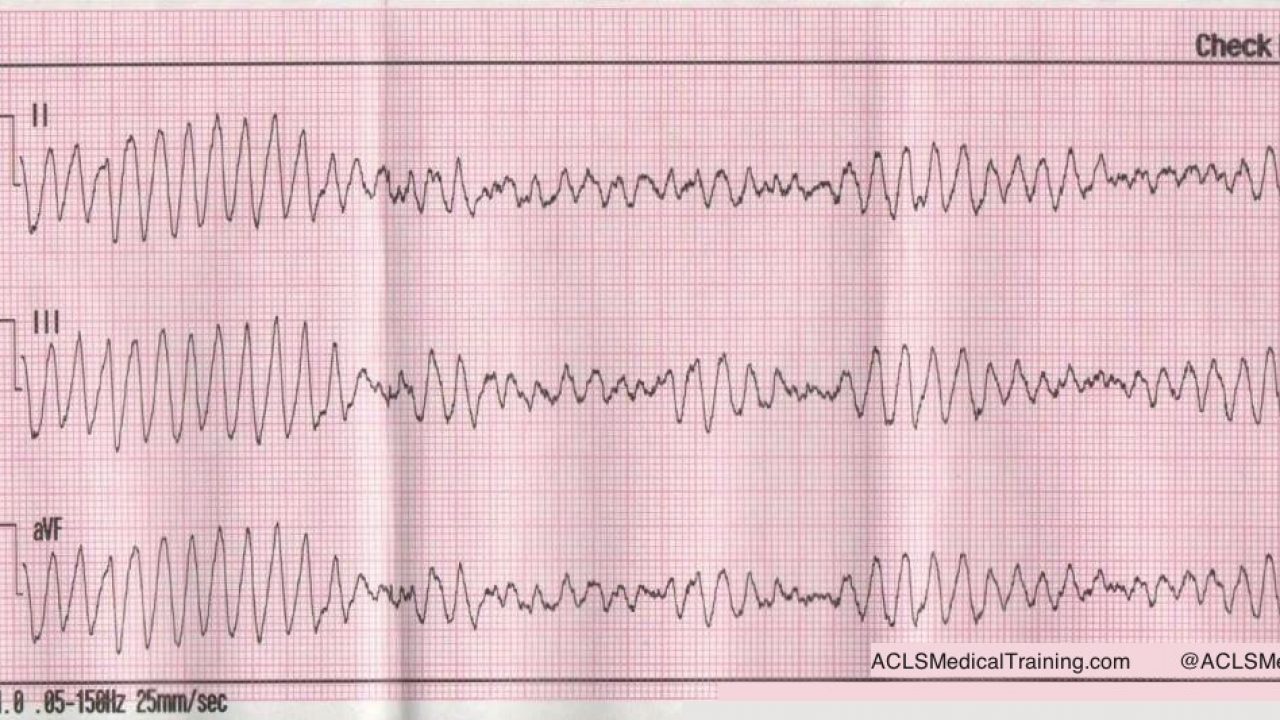
Ventricular Tachycardia V Fib V Tach

Such a condition arises mostly in people having valvular hear disease.
Ventricular tachycardia v fib v tach. Ventricular tachycardia is an unusually fast heartbeat that starts in the lower part of your heart the ventricles it s sometimes called vt or v tach. There are two types. What is a. In this condition the heartbeat is so fast and irregular that.
Ventricular tachycardia v tach is treated similarly to v fib. Ventricular tachycardia vtach ventricular tachycardia is a medical condition which is associated with the hearts irregular electrical impulses. The difference is that ventricular tachycardia continues to make the heartbeat regularly but it goes so fast that the heart never gets a chance to fill with blood. A healthy heart normally beats about 60 to 100 times a minute at rest.
What is ventricular tachycardia. This would be called polymorphic ventricular tachycardia. There s not an opportunity to build up the pressure so the blood stops flowing. Nonsustained v tach resolves on its own within 30 seconds whereas sustained v tach lasts more than 30 seconds inhibits blood flow and requires medical intervention mayo clinic.
They are atrial tachycardia monofocal or multifocal atrial fibrillation atrial flutter atrioventricular nodal re entry tachycardia atrioventricular re entry. This condition may also be called v tach or vt. Because the heart is beating too fast it can t fill up with enough blood. We also need to follow the acls guidelines for v tach.
So therapeutic management for ventricular tachycardia is to determine the cause and treat it it may be something so simple as an electrolyte abnormality or an mi. Difference between ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation definition. Ventricular tachycardia vs ventricular fibrillation arrhythmia means irregular cardiac rhythm and slow arrhythmias are called bradyarrhythmias and fast ones are called tachyarrhythmias there are various types of arrhythmias. Ventricular tachycardia is a heart rhythm disorder arrhythmia caused by abnormal electrical signals in the lower chambers of the heart ventricles.