Ventricular Fibrillation V Fib Ekg

5 in vf the etiology of arrest is often attributed to either acute ischemia or non ischemic arrhythmia.
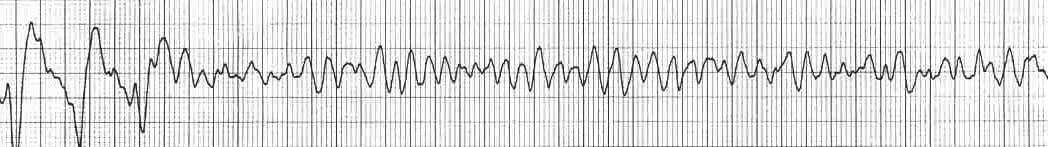
Ventricular fibrillation v fib ekg. This is followed by death in the absence of treatment. Includes ekg practice tracings and assessment tips. As a result the heart cannot pump blood. 8 although vf appears as a chaotic and disorganized rhythm characteristics of the ventricular fibrillation waveform such as.
Symptoms of both afib and vfib are shortness of breath dizziness nausea and chest pain. It is due to disorganized electrical activity. Ventricular fibrillation v fib or vf is an abnormal heart rhythm in which the ventricles of the heart quiver instead of pumping normally. V fib ventricular fibrillation is an emergency that requires immediate medical attention.
Ventricular fibrillation vf is the the most important shockable cardiac arrest rhythm. Atrial fibrillation is caused by irregular electrical impulses in the atria and ventricular fibrillation is caused by irregular electrical impulses in the ventricles. They are atrial tachycardia monofocal or multifocal atrial fibrillation atrial flutter atrioventricular nodal re entry tachycardia atrioventricular re entry. The ventricles suddenly attempt to contract at rates of up to 500 bpm.
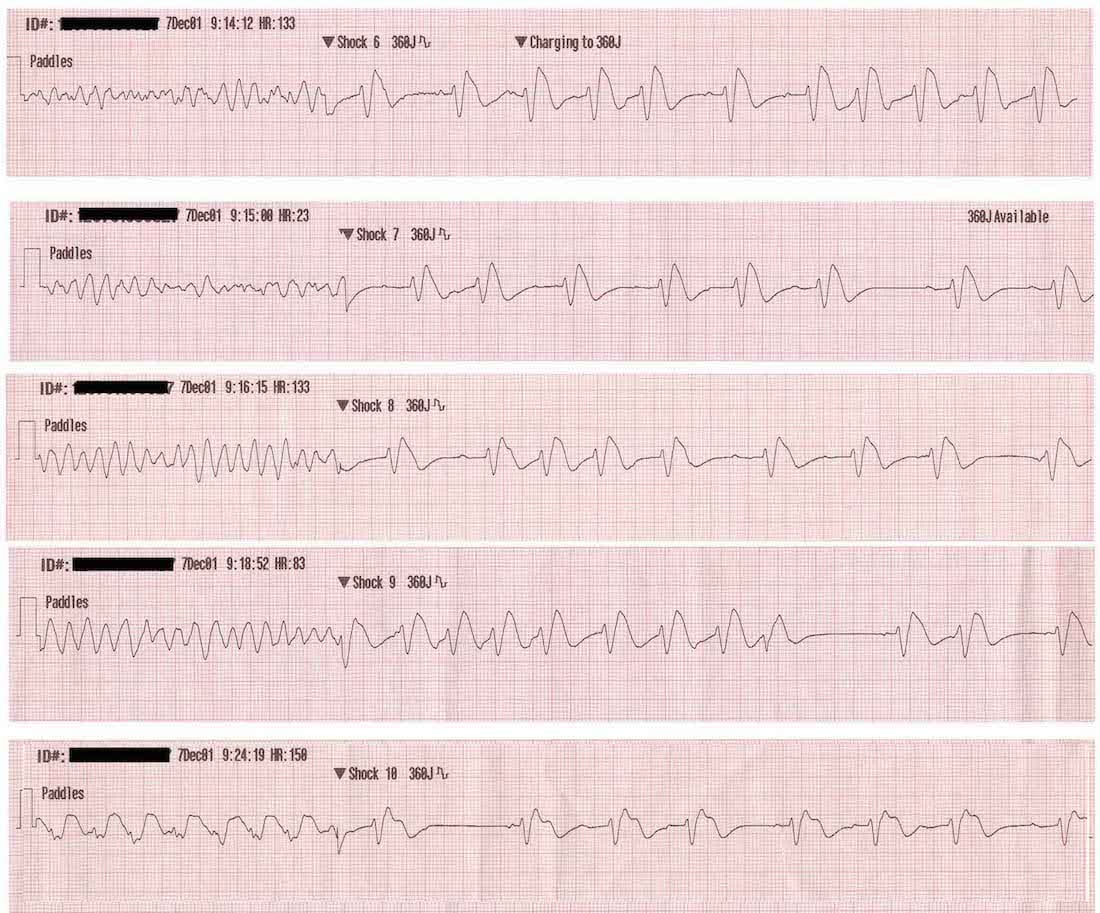
Ventricular fibrillation vf or v fib is the most common initial heart rhythm in patients with out of hospital cardiac arrest ohca and the most salvageable one. Ventricular tachycardia vs ventricular fibrillation arrhythmia means irregular cardiac rhythm and slow arrhythmias are called bradyarrhythmias and fast ones are called tachyarrhythmias there are various types of arrhythmias. This is pathognomonic unique to ventricular fibrillation and must not be confused with any other arrhythmia. Ventricular fibrillation is initially found in about 10 of.
Ecg features of ventricular fibrillation. Ventricular fibrillation is the most commonly identified arrhythmia in cardiac arrest patients. Ekg reference guide for ventricular fibrillation. Atrial fibrillation afib and ventricular fibrillation vfib are both a type of abnormal heart rhythm arrhythmia.
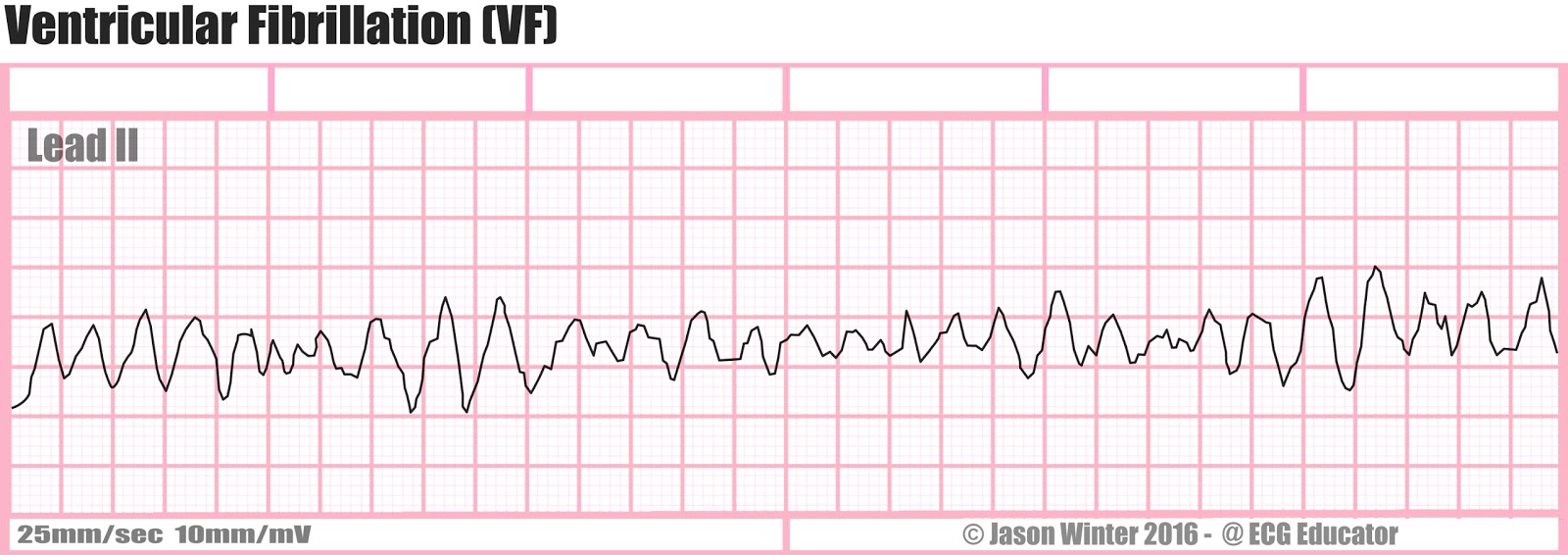
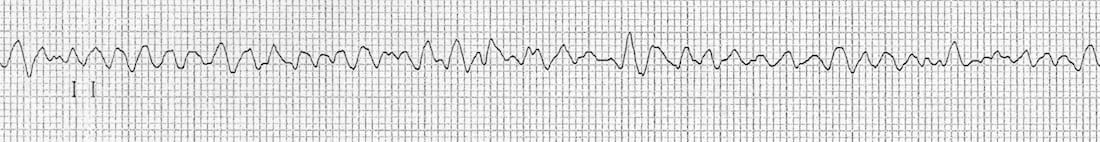
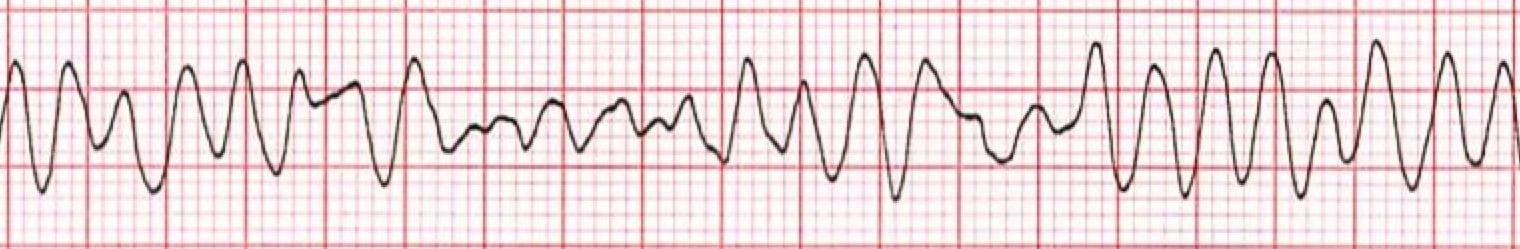
This rapid and irregular electrical activity renders the ventricles unable to contract in a synchronised manner resulting in immediate loss of cardiac output. The ecg shows irregular waves with varying morphology and amplitude. The ecg criteria to diagnose ventricular fibrillation vfib on a 12 lead ecg is discussed including a brief discussion of treatment using automated external defibrillators aed and icds. Ventricular fibrillation results in cardiac arrest with loss of consciousness and no pulse.
It is a frequent cause of sudden cardiac death.