V Fib Vs A Fib Ekg

The course provides training on the key features of an ekg tracing.
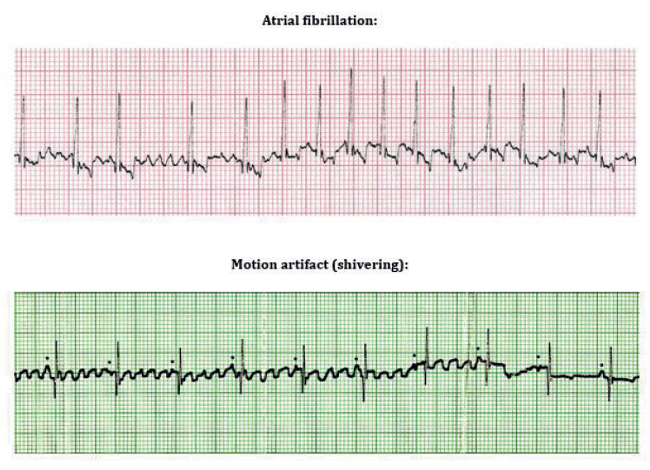
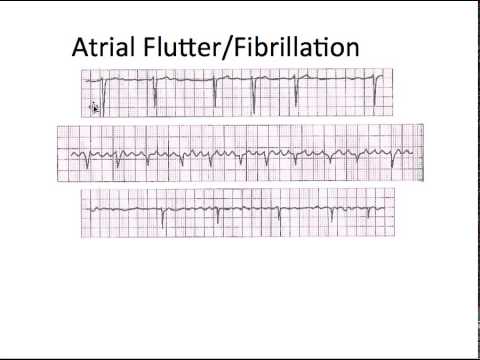
V fib vs a fib ekg. One of the main differences between these two heart conditions is that ventricular fibrillation is life threatening if treatment isn t begun immediately while atrial fibrillation generally is not immediately life threatening but can cause problems with the heart function that are very dangerous if not treated effectively. A doctor can identify some types of atrial fibrillation by looking at an electrocardiogram. The mother rotor then gives rise to propagating unstable daughter wavefronts which results in the chaotic electrical activity seen on the ecg. Atrial fibrillation is caused by irregular electrical impulses in the atria and ventricular fibrillation is caused by irregular electrical impulses in the ventricles.
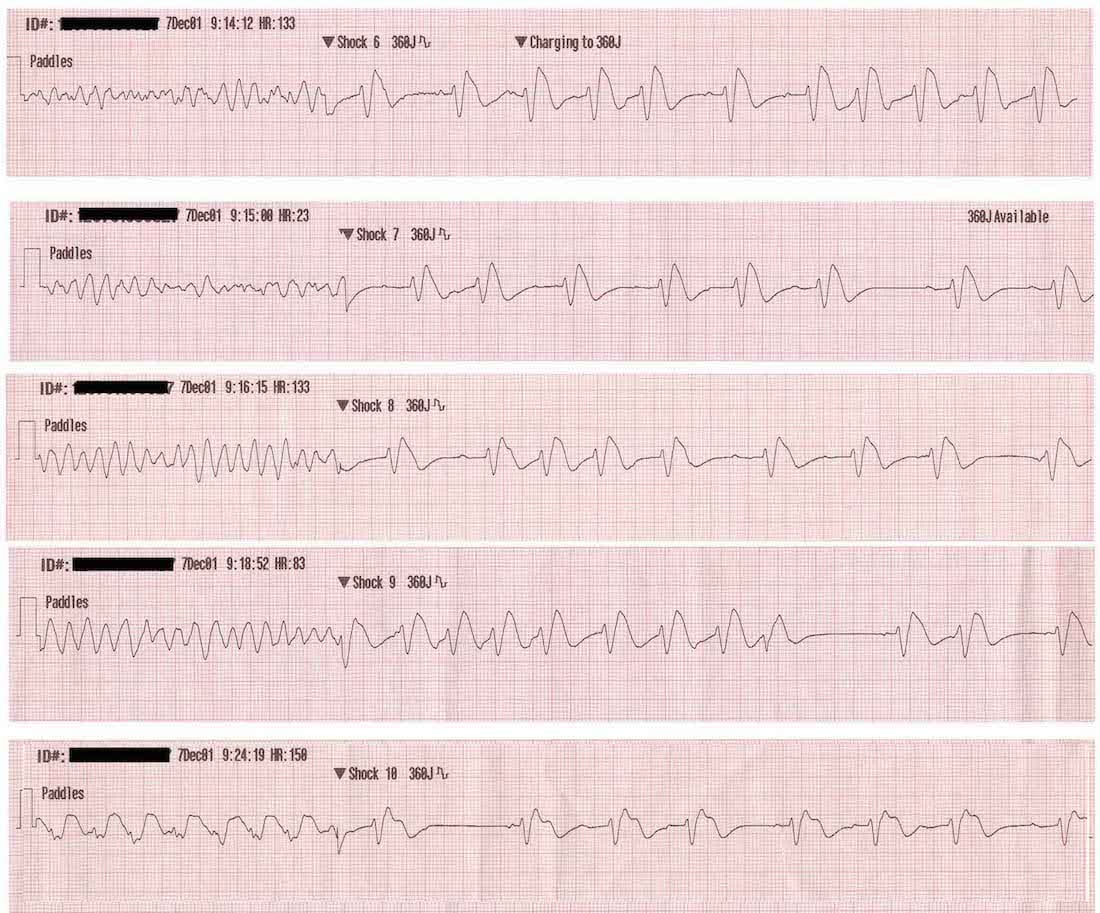
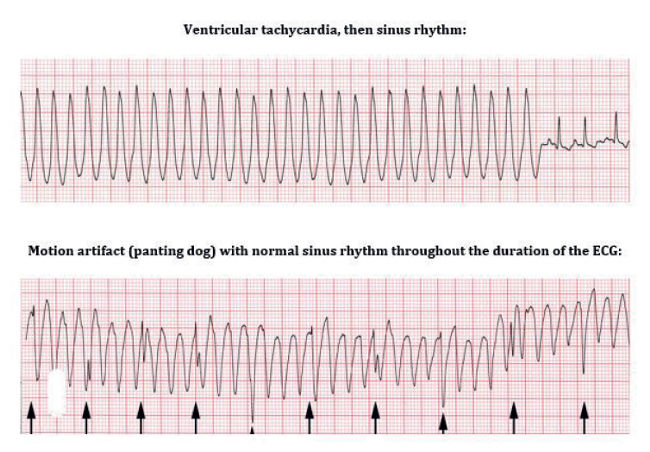
No p wave qrs complex or t wave can be seen. Atrial fibrillation or a fib can lead to fatal heart complications if it reaches a severe enough stage. The ecg shows irregular waves with varying morphology and amplitude. Ventricular fibrillation vfib ventricular fibrillation vfib is a medical condition in which the heart beats in an abnormal rhythm.
Atrial fibrillation occurs in the heart s upper two chambers also known as the atria. A good starting point for learning about v fib and other types of ekg interpretation is our ekg basics training course. Ventricular fibrillation occurs in the heart s lower two chambers known as the ventricles. These features include observing p wave forms measurement of ekg intervals and segments assessment of rhythm calculating heart rate and the evaluation of other relevant wave segments.
The lower heart chambers show quivering activity and the heart is unable to pump any blood leading to cardiac arrest. The first upward pulse of the ekg signal the p wave is formed when the atria the two upper chambers of the heart contract to pump blood into the ventricles. A characteristic sign of a fib is the absence of a p wave in the ekg signal. The fibrillation is maintained by re entry circuits formed by some of the wavelets.
Symptoms of both afib and vfib are shortness of breath dizziness nausea and chest pain. This is pathognomonic unique to ventricular fibrillation and must not be confused with any other arrhythmia. Ventricular fibrillation with low amplitude waves less than 3 mm is called fine vf. Fine ventricular fibrillation is even more dangerous than coarse ventricular fibrillation because there is even less contractility of the myocardium which results in a smaller amplitude.