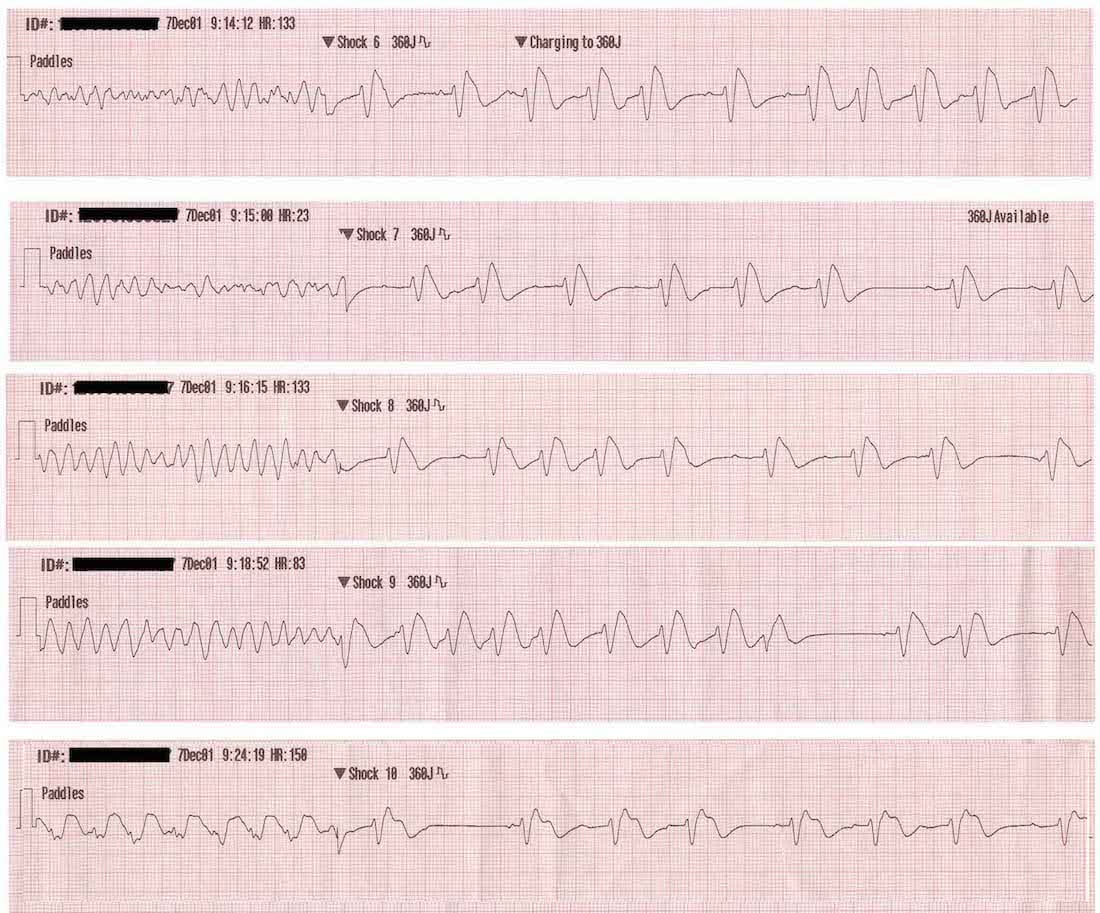
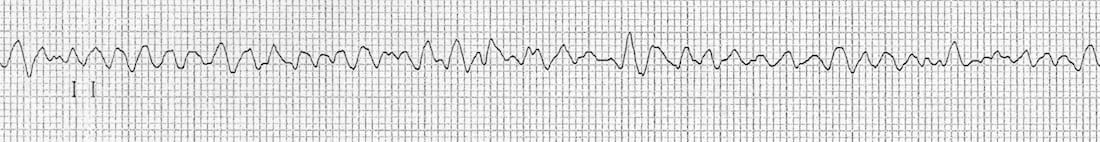
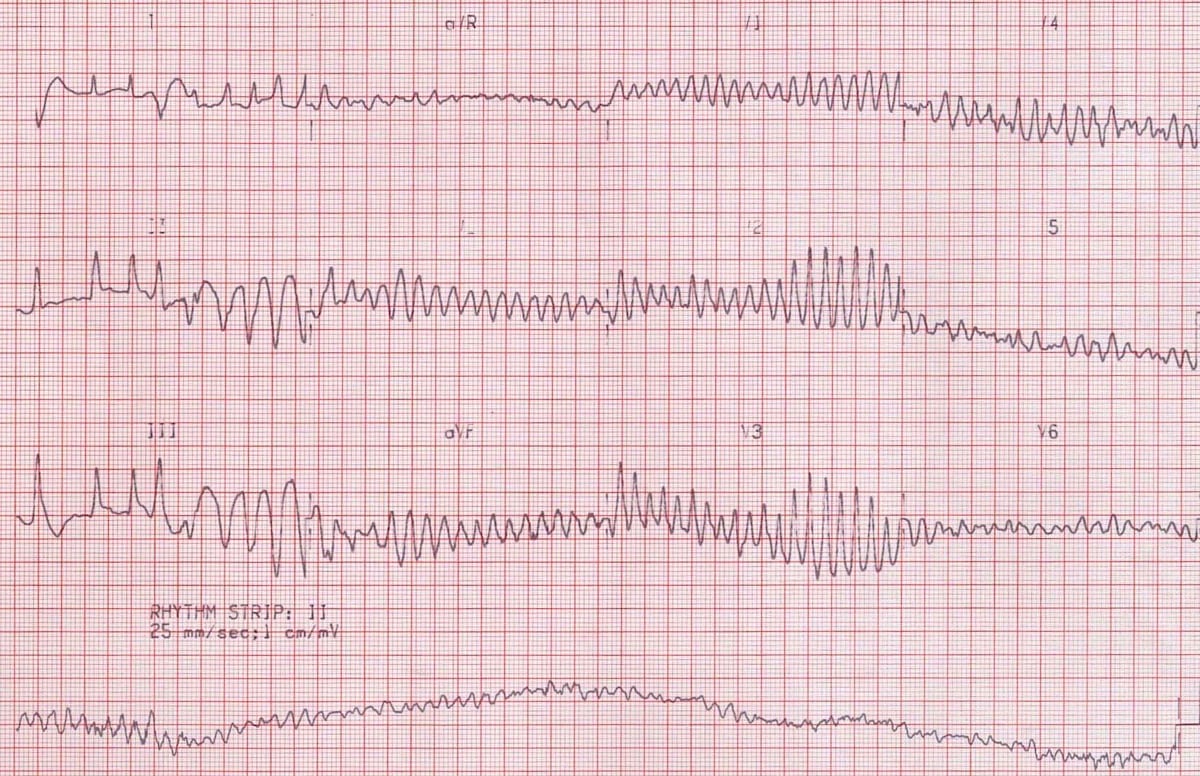
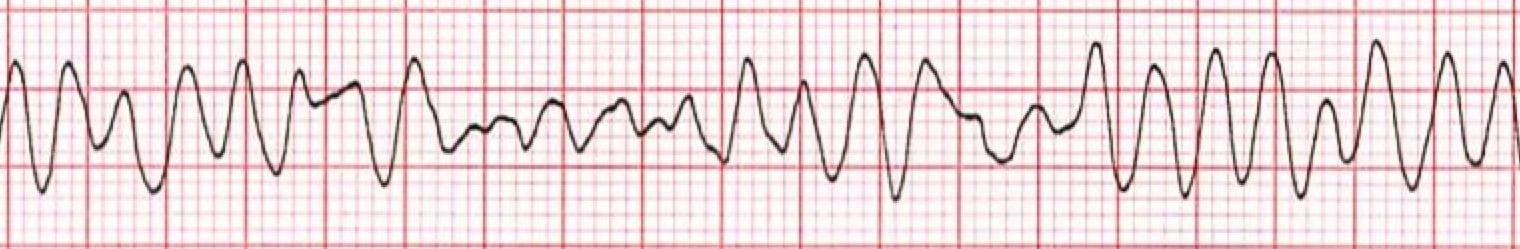
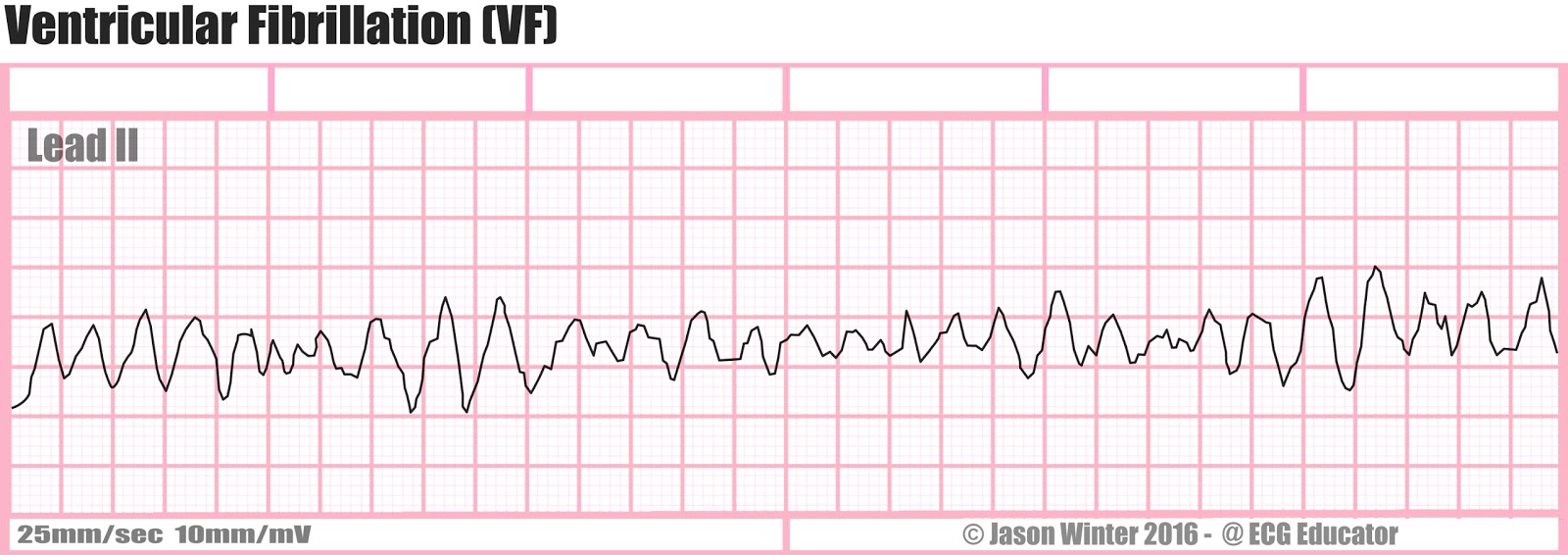
V Fib Ecg

No p wave qrs complex or t wave can be seen.
V fib ecg. Prevalence of atrial fibrillation correlates strongly with age. This is followed by death in the absence of treatment. These features include observing p wave forms measurement of ekg intervals and segments assessment of rhythm calculating heart rate and the evaluation of other relevant wave segments. The ecg shows irregular waves with varying morphology and amplitude.
What is ventricular fibrillation. 03 10 ventricular fibrillation v fib 03 11 1st degree av heart block 03 12 2nd degree av heart block type 1 mobitz i wenckebach. Ecg features of ventricular fibrillation. The mother rotor then gives rise to propagating unstable daughter wavefronts which results in the chaotic electrical activity seen on the ecg.
Definitions causes risk factors ecg diagnosis and management. Ventricular fibrillation v fib or vf is a life threatening arrhythmia where the muscle fibers in the heart s ventricles d. Atrial fibrillation is the most common pathologic tachyarrhythmia only sinus tachycardia is more common. Ventricular fibrillation results in cardiac arrest with loss of consciousness and no pulse.
The fibrillation is maintained by re entry circuits formed by some of the wavelets. A good starting point for learning about v fib and other types of ekg interpretation is our ekg basics training course. Mother rotor mechanism in which a stable re entry circuit is formed the mother rotor. The ecg criteria to diagnose ventricular fibrillation vfib on a 12 lead ecg is discussed including a brief discussion of treatment using automated external defibrillators aed and icds.
This is pathognomonic unique to ventricular fibrillation and must not be confused with any other arrhythmia. Ventricular fibrillation v fib or vf is an abnormal heart rhythm in which the ventricles of the heart quiver instead of pumping normally.